How Do Neap Tides Occur? A Simple Explanation of Lunar TidesTides are the regular rise and fall of sea levels caused by the gravitational pull of the moon and the sun. Among the different types of tides, neap tides are known for their minimal tidal range. But what exactly causes neap tides, and why do they happen only at certain times of the month? This topic breaks down the process in clear and easy-to-understand terms.
What Are Neap Tides?
Neap tides are a type of tide that occurs when the difference between high and low tide is at its smallest. These tides take place twice a month during the first and third quarters of the moon. When neap tides occur, high tides are not as high as usual, and low tides are not as low.
This smaller tidal range happens because the moon and the sun exert gravitational forces that partially cancel each other out during these lunar phases.
The Role of the Moon and Sun in Tides
Tides are mainly controlled by the gravitational force of the moon, which pulls water on Earth toward it, creating a bulge or high tide. At the same time, a second high tide occurs on the opposite side of the Earth due to inertia. The sun also influences tides, but its pull is weaker compared to the moon’s effect because it is much farther away.
The combined gravitational forces of the sun and moon can either strengthen or weaken the tides depending on their positions relative to the Earth.
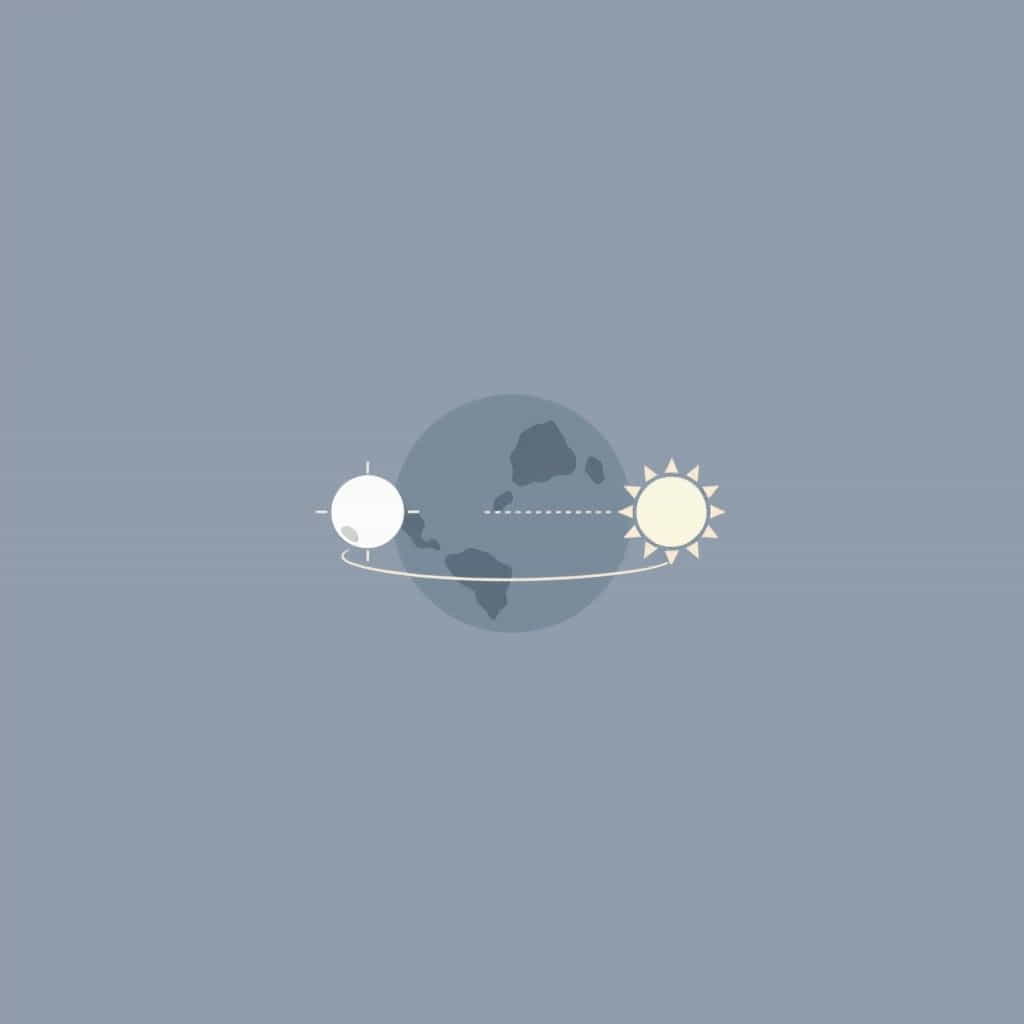
How Neap Tides Form
Neap tides form when the sun and the moon are at a 90-degree angle to each other, with Earth at the center. This alignment happens during the first quarter and third quarter phases of the moon. Because the gravitational forces of the moon and sun are pulling water in different directions, they partially counteract each other.
As a result, the ocean bulge is less pronounced, and we experience lower high tides and higher low tides a neap tide.
Neap Tides vs. Spring Tides
Understanding neap tides becomes easier when compared to spring tides, another regular tidal occurrence.
| Feature | Neap Tides | Spring Tides |
|---|---|---|
| Tidal Range | Smallest (least difference) | Largest (most difference) |
| Occurs During | First & third quarter moons | New moon & full moon |
| Gravitational Pull | Forces cancel each other | Forces combine and strengthen |
Spring tides occur when the moon and sun are aligned (either on the same side or opposite sides of Earth), so their gravitational forces combine, leading to stronger tides.
How Often Do Neap Tides Happen?
Neap tides are part of the lunar cycle, which takes about 29.5 days to complete. This means neap tides occur every 14 to 15 days, or twice a month, always between two spring tide periods.
The exact timing of neap tides can be predicted using tidal charts and calendars based on the lunar phases.
Where Are Neap Tides Most Noticeable?
Neap tides can be observed anywhere tides exist, but their effects are more noticeable in coastal areas with large tidal ranges. Some regions around the world where neap tides have a visible impact include
-
The Bay of Fundy in Canada
-
The Bristol Channel in the United Kingdom
-
Mont-Saint-Michel in France
In these areas, the contrast between spring and neap tides can affect marine life, coastal activities, and human planning.
The Impact of Neap Tides on Marine and Human Activity
Neap tides might not seem dramatic, but they still have important consequences
1. Navigation and Fishing
Shallower water levels during neap tides can make it harder for boats to move in and out of harbors. Fishermen may also plan their activities around the lower movement of water.
2. Coastal Construction
Engineers consider neap and spring tides when designing sea walls, docks, or flood barriers. Accurate knowledge of tidal behavior is key for long-term planning.
3. Marine Ecosystems
Some marine species depend on stronger or weaker tides for feeding and reproduction. Neap tides influence where and when certain fish or crustaceans can move.
Can Neap Tides Be Predicted?
Yes, neap tides follow a predictable pattern tied to the lunar phases. Scientists and maritime experts use tidal prediction charts to determine the timing and strength of tides for every coastal region.
These forecasts are based on long-term observations and mathematical models that take into account the positions of the moon and sun.
Do Neap Tides Vary Around the World?
The size and strength of neap tides can vary depending on location. Factors that affect this include
-
Shape of the coastline
-
Depth of the ocean near shore
-
Latitude
-
Earth’s tilt and rotation
For example, in narrow bays or estuaries, the effects of neap tides might be more noticeable than in wide open coastlines.
Summary
Neap tides are a fascinating part of Earth’s natural rhythm, occurring twice a month when the moon and sun are at right angles. Their gravitational forces reduce the tidal range, resulting in gentler ocean movement. While not as dramatic as spring tides, neap tides still play a significant role in marine navigation, coastal management, and the behavior of sea life.
By understanding how neap tides occur, we gain deeper insight into how the Earth, moon, and sun work together to shape our planet’s waters in subtle but powerful ways.